用於自動化訂單履行的機器人系統
Optimizing Warehouse Layout for Robotic Integration
Effective warehouse design is paramount when incorporating robotic systems. A well-planned layout considers the movement patterns of robots, ensuring unobstructed pathways and minimizing potential collisions. This strategic placement maximizes efficiency, allowing robots to navigate the space with ease and speed, ultimately reducing operational bottlenecks and increasing throughput. Careful consideration should be given to the flow of goods and the positioning of storage areas to facilitate seamless integration with robotic handling systems. The goal is to create a space that facilitates the smooth and continuous operation of the robotic systems, thereby improving overall warehouse productivity.
Robotic Arm Selection and Placement
Choosing the right robotic arms for specific tasks is crucial. Different robotic arms excel at diverse operations, from picking and packing to material handling. Factors such as payload capacity, reach, speed, and precision must be carefully evaluated to ensure the selected arms are adequately equipped for the intended tasks within the warehouse environment. Proper placement of these arms within the warehouse layout is equally important, ensuring optimal accessibility to work areas and minimizing unnecessary movement.
Careful consideration of the specific tasks performed by the robotic arms is vital. For example, if the robotic arms need to reach high shelves, then their placement and design must accommodate this need. Similarly, if the arms are primarily involved in ground-level tasks, their positioning should optimize their access to the goods and minimize unnecessary travel time.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Their Integration
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) play a significant role in transporting goods between different zones within the warehouse. The integration of AGVs into the overall design is critical for efficient material flow. The design should incorporate designated lanes and pathways for these vehicles, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted movement. This seamless integration ensures that AGVs can move materials efficiently and effectively, thereby reducing transit time and boosting overall warehouse performance.
Inventory Management Systems and Robotics
Modern inventory management systems are essential for optimizing the utilization of robotic systems. These systems provide real-time data on inventory levels, locations, and movement, enabling robotic systems to precisely locate and retrieve items. This integration allows for more accurate and faster order fulfillment. The data feeds from these systems empower robotic systems to perform tasks with greater precision, minimizing errors and ensuring a high level of accuracy in the picking and packing process. Accurate inventory management is a key component in the success of a warehouse incorporating robotic systems.
Safety Protocols and Redundancy in Robotic Systems
Ensuring worker safety and the reliability of robotic systems are paramount. Robust safety protocols must be implemented to prevent accidents and minimize risks. These protocols should include clear demarcated zones for human workers and robots, emergency stop mechanisms, and regular maintenance schedules. Redundancy in certain robotic systems is also important. Having backup systems or alternative routes ensures that operations can continue even if one system fails. This proactive approach safeguards against disruptions and maintains operational continuity.
Data Analysis and Continuous Improvement
Data analysis plays a crucial role in evaluating the performance of robotic systems and optimizing warehouse operations. Analyzing data from robotic systems, inventory management, and other sources allows for the identification of bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach enables continuous optimization of the warehouse design and robotic systems to enhance productivity and reduce costs. By continuously evaluating and adjusting the system based on data, warehouses can stay ahead of the curve in the ever-evolving landscape of logistics and automation.
Future Trends and Considerations for Robotic Integration
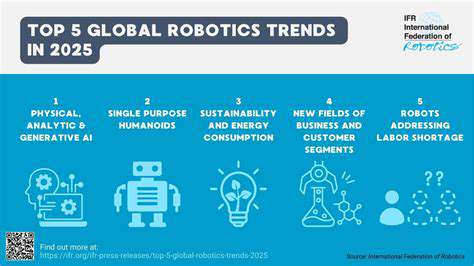
Technological Advancements in the Field
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize numerous aspects of the field, from data analysis and predictive modeling to automation of tasks. AI-powered tools will likely become increasingly sophisticated, enabling more efficient and accurate processes. This includes the development of algorithms that can identify complex patterns and insights within data sets, leading to better decision-making and optimized resource allocation.
Furthermore, the integration of machine learning (ML) models into existing workflows promises to enhance the accuracy and speed of various operations. These advancements will not only streamline existing procedures but also open up new possibilities for innovation and discovery.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
As the field increasingly relies on data collection and analysis, robust security measures will be paramount to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with privacy regulations. Data breaches and unauthorized access can have significant consequences, impacting not only the integrity of research but also public trust.
Implementing strong encryption protocols and access controls is crucial to safeguarding data. Moreover, ongoing education and training for personnel handling sensitive information are essential to prevent unintentional vulnerabilities and maintain data privacy.
Ethical Implications of Emerging Technologies
The integration of new technologies raises profound ethical considerations that require careful examination and discussion. Issues such as algorithmic bias, the potential for misuse, and the impact on human jobs need to be addressed proactively.
Ethical frameworks and guidelines should be developed to ensure responsible innovation and mitigate potential risks. These frameworks should consider the societal implications of new technologies and promote fairness, transparency, and accountability.
The Role of Interdisciplinary Collaboration
The complexities of the field necessitate a collaborative approach involving experts from diverse disciplines. Interdisciplinary teams can bring together varied perspectives, expertise, and methodologies, leading to more comprehensive and innovative solutions.
Collaboration across different sectors, such as engineering, social sciences, and the humanities, will be vital to address the multifaceted challenges and opportunities ahead. This collaborative approach can lead to more holistic and nuanced understandings of the field and its implications.
Adapting to Changing Regulatory Landscapes
The evolving regulatory environment surrounding the field demands continuous adaptation and compliance. Keeping abreast of new regulations and policies is crucial for maintaining ethical operations and avoiding legal issues.
Staying informed about legal requirements and industry best practices is essential for navigating this dynamic landscape. This includes understanding and adhering to data protection regulations, intellectual property rights, and other relevant legal frameworks.
Investment in Infrastructure and Resources
Adequate investment in infrastructure, including computational resources and specialized equipment, is critical for supporting research and development in the field. This investment will ensure that the field can effectively utilize advanced technologies and maintain its momentum.
The Importance of Workforce Development
A skilled and adaptable workforce is essential for the continued success and innovation in the field. Investing in training and development programs for current and future professionals is paramount to ensure expertise and competence are maintained.
Upskilling and reskilling initiatives are necessary to prepare the workforce for the evolving demands of the field, including the increasing integration of AI and automation. Continuous learning and adaptability are crucial for professionals to thrive in this dynamic environment.