Tuân thủ quy định: Tiêu chuẩn và nghĩa vụ về khả năng truy xuất nguồn gốc chuỗi cung ứng
Công nghệ và Cơ sở hạ tầng
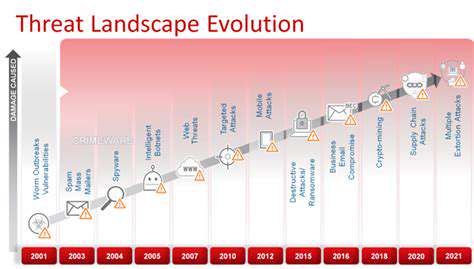
Chọn Công nghệ Theo dõi Phù hợp
Chọn công nghệ theo dõi phù hợp là rất quan trọng cho việc triển khai thành công. Điều này đòi hỏi phải xem xét kỹ lưỡng nhu cầu cụ thể của tổ chức bạn, bao gồm các loại dữ liệu được theo dõi, khối lượng dữ liệu
Đề cập đến Thách thức và Phương Pháp Tốt nhất cho Tuân thủ

Xử lý Hạn chế về Nguồn lực
Quản lý dự án hiệu quả thường phải đối mặt với những hạn chế đáng kể về nguồn lực
Xu hướng tương lai và Bối cảnh Theo dõi đang thay đổi

Các Mô hình ngôn ngữ dựa trên AI nổi lên
Sự phát triển nhanh chóng của trí tuệ nhân tạo (AI) đang là cơ sở cho
THE END
More about Tuân thủ quy định: Tiêu chuẩn và nghĩa vụ về khả năng truy xuất nguồn gốc chuỗi cung ứng
- Những điều cần lưu ý khi mua đồ gỗ trực tuyến
- Bàn ăn gỗ tốt nhất cho những bữa tiệc gia đình lớn
- Cách chọn đồ gỗ cho ngôi nhà mang phong cách Zen
- Ưu điểm của đồ nội thất gỗ lắp ghép cho không gian sống linh hoạt
- Cách tạo phong cách công nghiệp sang trọng với đồ gỗ
- Cách chọn đồ gỗ cho phòng khách gia đình
- Cách làm cho đồ gỗ của bạn bền hơn với việc chăm sóc đúng cách
- Cách thêm nét sang trọng cho ngôi nhà của bạn với đồ gỗ
- Lợi ích của việc sử dụng hoàn thiện gỗ tự nhiên cho đồ nội thất của bạn
- Cách kết hợp đồ nội thất gỗ với trang trí cổ điển
- Những lợi ích hàng đầu khi chọn đồ nội thất gỗ tự nhiên cho ngôi nhà của bạn
- Theo dõi thời gian thực hàng hóa vận chuyển trong container