可持续供应链和碳足迹减排工具
Identifying Emission Sources
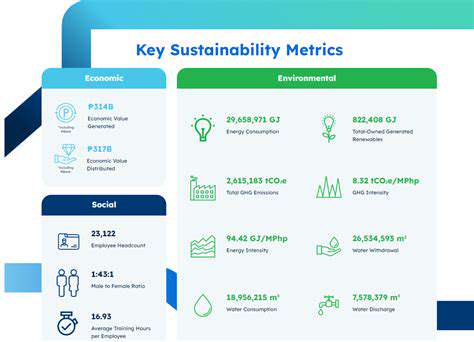
Identifying the specific sources of emissions is crucial for effective mitigation strategies. This involves a thorough analysis of various potential contributors, ranging from industrial facilities and transportation networks to residential energy consumption. Detailed inventorying of emissions from each source is essential for accurate quantification and targeted interventions. Understanding the specific processes and technologies involved in each source type allows for the development of tailored solutions to reduce emissions.
Furthermore, factors like geographical location, time of day, and weather patterns can influence emission levels. Careful consideration of these variables is critical for a comprehensive understanding of emission profiles and the development of accurate emission models.
Quantifying Emission Levels
Accurate quantification of emissions is a fundamental step in environmental management. This involves measuring the amount of pollutants released into the atmosphere, often using sophisticated instrumentation and advanced modeling techniques. Precise measurements are crucial for determining the environmental impact of various activities and for setting appropriate regulatory standards. Quantifying emissions also allows for the comparison of different sources and activities, providing valuable insights into their relative contributions to overall pollution.
Developing Emission Models
Emission models play a vital role in predicting and understanding the behavior of emissions over time and space. These models integrate various factors, including source characteristics, meteorological conditions, and atmospheric transport patterns to project emissions. This allows for the estimation of future emission scenarios and the evaluation of the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
These models are complex and require substantial data to ensure accuracy and reliability. The accuracy of the models is directly related to the precision of the data used in their development, which highlights the importance of accurate and consistent data collection.
Implementing Monitoring and Reporting Systems
Robust monitoring and reporting systems are essential for tracking emissions over time. Implementing these systems requires the establishment of consistent procedures for data collection, analysis, and reporting. These systems facilitate the identification of trends, patterns, and anomalies in emission levels and help to quantify the success of mitigation efforts.
Effective monitoring and reporting systems also provide transparency and accountability, allowing stakeholders to track progress and hold responsible parties accountable for their emissions. Real-time data visualization tools can further enhance the accessibility and understanding of emission trends and patterns.
Analyzing Emission Impacts
Analyzing the impacts of emissions on the environment and human health is crucial for prioritizing mitigation efforts. This involves evaluating the potential for air pollution, climate change, and other adverse effects. A detailed understanding of the potential impacts is essential for informed decision-making and the development of effective policies. Careful consideration of the cumulative effects of emissions from various sources is essential for evaluating overall environmental risk.
This analysis often involves integrating scientific data with socioeconomic factors to understand the broader impacts on communities and ecosystems. Thorough assessments help prioritize mitigation efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Web scraping, while a powerful tool for data extraction, carries inherent ethical implications. Respecting website terms of service and robots.txt files is paramount. These directives dictate how web crawlers should interact with the site, and ignoring them can lead to serious repercussions, including account suspension or legal action. Understanding and adhering to these guidelines is crucial for responsible scraping practices.
Collaboration and Partnerships for Systemic Change
Strengthening Supply Chains Through Collaboration
Collaboration is crucial for building resilient and sustainable supply chains. By working together, businesses can share knowledge, resources, and best practices, ultimately leading to improved efficiency, reduced waste, and a more environmentally conscious approach to manufacturing and distribution. This collaborative approach fosters innovation and allows companies to address complex challenges collectively, driving positive change throughout the entire system.
Partnerships between manufacturers, suppliers, retailers, and even NGOs can create a powerful network for sustainable development. Sharing data on environmental impact, resource consumption, and social responsibility practices can help identify areas for improvement and drive collective action towards more sustainable practices. This collaborative effort is essential for achieving systemic change.
The Role of Technology in Facilitating Partnerships
Modern technology plays a critical role in enabling effective collaboration and partnerships for sustainable supply chains. Digital platforms can connect businesses and stakeholders, enabling seamless information sharing, real-time tracking of products, and improved communication channels. This facilitates transparency and accountability, allowing all parties to understand the entire lifecycle of a product, from raw material sourcing to final delivery.
Implementing robust data management systems and utilizing analytics tools can help identify trends, predict potential issues, and optimize resource allocation. This data-driven approach empowers businesses to make informed decisions, reduce risks, and create a more sustainable supply chain model.
Partnerships with NGOs for Social Responsibility
Partnerships with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are essential for addressing the social responsibility aspects of sustainable supply chains. NGOs possess expertise in areas such as fair labor practices, worker safety, and community development, offering valuable insights and support to companies seeking to improve their social impact. Collaborating with NGOs allows businesses to mitigate risks associated with human rights violations and ensure ethical treatment of workers throughout the supply chain.
Working with NGOs helps companies develop and implement robust social responsibility programs that promote fair wages, safe working conditions, and community engagement. This collaborative approach fosters a more equitable and just supply chain model, ensuring the well-being of workers and communities.
Government Regulations and Incentives for Collaboration
Government regulations and incentives can play a significant role in fostering collaboration and partnerships for systemic change in sustainable supply chains. Clear regulations regarding environmental standards, labor laws, and ethical sourcing practices can create a level playing field for businesses and encourage adoption of sustainable practices.
Furthermore, incentives such as tax breaks, grants, and subsidies for companies that adopt sustainable practices can motivate businesses to invest in new technologies and collaborate with others to achieve shared goals. Government support can help create a supportive environment for sustainable supply chains to flourish.
Building Trust and Transparency in Supply Chains
Building trust and transparency is fundamental to successful collaboration and partnerships in sustainable supply chains. Transparency in the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final delivery, helps build trust among stakeholders. This includes disclosing information regarding environmental impact, labor practices, and ethical sourcing.
Open communication channels and accessible data are crucial for fostering transparency. Businesses can use technology to enhance visibility and provide greater access to information about their supply chains. This increased transparency promotes accountability and allows stakeholders to hold each other responsible for their actions.
Measuring and Monitoring Progress Towards Sustainability
Measuring and monitoring progress towards sustainability is critical for evaluating the effectiveness of collaboration and partnerships. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) related to environmental impact, social responsibility, and economic performance can help track progress and identify areas for improvement. Regular reporting and data sharing among partners are crucial for monitoring progress and ensuring accountability.
Using standardized metrics and reporting frameworks enables stakeholders to compare performance, identify best practices, and drive continuous improvement. This ongoing monitoring and evaluation process ensures that collaborative efforts are effectively contributing to systemic change in the car industry's sustainable supply chains.
Community Engagement and Education for Sustainable Practices
Engaging local communities and providing education on sustainable practices is crucial for building a sustainable supply chain ecosystem. Involving communities in the supply chain process can create opportunities for local economic development and ensure that the benefits of sustainability are shared widely. This engagement also creates a sense of ownership and responsibility among all stakeholders.
Education programs can empower communities and raise awareness about the importance of sustainable practices. This knowledge transfer promotes a broader understanding of the environmental and social impact of supply chain decisions, ultimately fostering a more responsible and sustainable future for the car industry.