Diving Deep Into the Characteristics of Various Wood Types
Hardwood vs. Softwood: The Fundamental Distinction
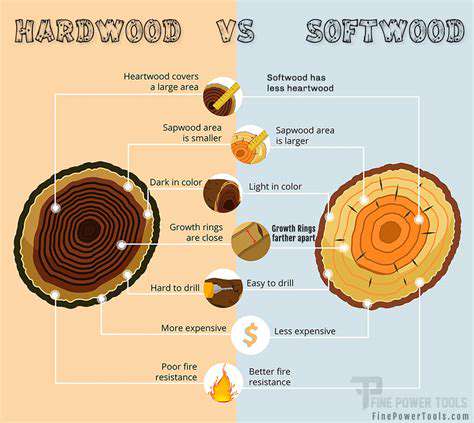
Understanding the Basics of Hardwood and Softwood
Wood is fundamentally categorized into two main types: hardwood and softwood. Understanding these classifications is essential for various applications, including construction, furniture making, and even musical instrument manufacturing. Hardwood typically comes from deciduous trees, which lose their leaves annually, while softwood is derived from coniferous trees that retain their foliage year-round.
The differences between hardwood and softwood extend beyond just their names. Characteristics such as density, grain patterns, and uses vary significantly between the two. Generally, hardwood tends to be denser and more durable, making it an ideal choice for high-quality furniture and flooring, while softwood is often lighter and more suitable for construction and woodworking projects.
A key factor that influences these distinctions is the growth rate of the trees. Hardwoods usually grow more slowly than softwoods, leading to a tighter grain and higher density of the wood fibers. Such growth patterns significantly affect the wood's strength, appearance, and overall performance in different contexts. Knowing the characteristics of these two categories can greatly inform buying decisions for wood-based products.
Applications of Hardwood and Softwood in Various Industries
The choice between hardwood and softwood often depends on the intended application. Hardwoods are commonly used in applications requiring durability and aesthetic appeal, such as cabinetry, high-end furniture, and flooring. Their ability to withstand wear and tear while providing a refined finish makes them a preferred option for luxury items. For instance, species like oak, maple, and cherry have gained popularity in fine furnishings due to their beautiful grain and staining properties.
Softwoods, on the other hand, are frequently utilized in construction projects such as framing, roofing, and sheathing. Their quick growth cycle allows for cost-effective sourcing and widespread availability, making them ideal for large-scale building projects. Common softwood types like pine, cedar, and spruce are widely favored for their lightweight nature, making them easier to handle during construction.
Environmental Considerations in Wood Sourcing
An important aspect of the debate between hardwood and softwood is their impact on the environment. Sustainable sourcing of both types of wood is crucial in combating deforestation and promoting healthy ecosystems. Hardwoods, typically slower growing, can be more vulnerable to overharvesting, while softwoods are often managed in a more sustainable manner thanks to their rapid growth cycle.
Certain certifications help consumers make environmentally responsible choices. Organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) ensure that wood products are sourced from responsibly managed forests. This is especially important for hardwoods, which are at risk due to their slow regeneration rates. Choosing certified wood not only supports sustainable practices but also promotes the preservation of biodiversity within forested areas.
Key Factors for Selecting the Right Type of Wood
In choosing between hardwood and softwood for a project, various factors must be taken into account. First and foremost, understanding the specific requirements of the project—such as durability, appearance, and maintenance—is essential. Different woods offer unique benefits, and aligning these with your needs can significantly influence the outcome of your project. For example, if longevity is a priority, hardwoods may be the better choice for a long-lasting finish.
Cost also plays a significant role in the decision-making process. While hardwoods typically carry a higher price tag, their durability may justify the investment. Conversely, softwoods may provide a budget-friendly option for projects where extensive wear and tear is not a concern. Knowing your budget constraints is crucial when evaluating which type of wood to select for your needs.
Lastly, consider the aesthetic qualities that each type of wood brings to a project. Hardwoods usually present a more exquisite finish and a richer color palette, contributing to a luxurious ambiance. Softwoods, with their lighter shades and simpler grain patterns, can lend a more rustic or casual look. Ultimately, the choice between hardwood and softwood should reflect both functional and stylistic preferences, ensuring the final product perfectly suits its intended environment.
The Richness of Hardwoods

The Distinctive Features of Hardwoods
Hardwoods are characterized by their density and strength, making them excellent choices for furniture and flooring. This intrinsic sturdiness is often why hardwoods are preferred for high-traffic areas in homes. Many hardwood species also exhibit unique grain patterns and rich colors, adding aesthetic appeal to various applications.
Another defining feature of hardwoods is their durability. Hardwoods can withstand wear and tear over time, making them a long-term investment. For instance, oak, cherry, and maple are frequently chosen for their longevity and resilience, ensuring that pieces remain intact for generations.
Environmental Impact of Hardwoods
The harvesting of hardwoods plays a crucial role in environmental sustainability. Sustainable forestry practices aim to minimize deforestation and promote regrowth, ensuring that hardwoods can be enjoyed for years to come. Choosing hardwood products from responsibly managed forests can significantly reduce the ecological footprint associated with wood consumption.
Additionally, hardwoods contribute positively to carbon sequestration. As trees grow, they absorb carbon dioxide and help in reducing greenhouse gases. Therefore, investing in hardwood can also mean investing in a healthier planet.
Common Uses and Applications of Hardwoods
Hardwoods are often chosen for a variety of applications, including cabinetry, flooring, and fine furniture. They not only provide structural integrity but also enhance the visual appeal of spaces. Many artisans prefer hardwood due to its workability and ability to take on intricate designs.
Beyond aesthetics, hardwood species such as teak and mahogany are frequently utilized in outdoor furniture due to their resistance to moisture and insects. This versatility illustrates why hardwood is a coveted material across several industries. From residential to commercial applications, the richness of hardwoods shines through in their diverse usability.
The Economic Value of Hardwood Products
The economic aspect of hardwood products is significant, reflecting their premium pricing compared to softwoods. Hardwoods are often associated with luxury and quality craftsmanship, which can command higher prices in the market. This perceived value makes hardwoods a lucrative investment for both manufacturers and consumers.
Moreover, the market for hardwood has expanded, offering a variety of species that cater to different tastes and budgets. As environmental awareness grows, there is an increasing demand for ethically sourced hardwood products. This trend is likely to continue, creating new opportunities in the hardwood industry for sustainable practices.
The Versatility of Softwoods
Applications of Softwoods in Construction and Design
Softwoods, known for their lightweight nature and ease of workability, have become the cornerstone of modern construction practices. These woods, derived primarily from coniferous trees like pine, spruce, and cedar, are favored for structural applications, including beams and frames. Their natural abundance and rapid growth cycles also make them a sustainable choice for building, addressing both economic and environmental concerns.
In design contexts, softwoods offer both aesthetic versatility and functional attributes. The warm tones and varied grain patterns of woods such as Douglas fir and cedar enhance the beauty of interior spaces, making them popular choices for flooring, cabinetry, and decorative moldings. Designers often highlight the natural characteristics of softwoods, using them to create inviting spaces that blend rustic charm with modern elegance.
Furthermore, softwoods are advantageous in residential construction due to their superior insulating properties and sound-dampening qualities. Homes built with softwood framing, especially those insulated with eco-friendly materials, can provide a comfortable living environment while reducing energy costs. This combination of efficiency, comfort, and style continues to drive the demand for softwoods in residential projects.
Outside of traditional construction, the adaptability of softwoods extends into various industries, including furniture manufacturing and crafts. The ease of machining softwoods makes them ideal for intricate designs, allowing craftsmen to create unique pieces that captivate consumers. This versatility enables softwoods to maintain a significant presence in both contemporary and traditional furniture markets.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Softwoods
The environmental implications of using softwoods have increasingly gained attention in recent years, especially as global awareness of sustainability grows. Softwoods can be harvested responsibly, ensuring that forests remain healthy and productive. Sustainable forestry practices, such as selective logging and replanting efforts, allow for continuous wood production without causing ecosystem damage.
Additionally, using softwoods can result in lower carbon footprints compared to hardwood alternatives. Due to their faster growth rates, softwoods sequester carbon dioxide more rapidly, thus contributing positively to climate change mitigation. This characteristic makes them an appealing option for eco-conscious builders and consumers seeking to reduce their impact on the environment.
Moreover, many softwood species are naturally resistant to pests and decay, reducing the need for chemical treatments. This trait adds to their sustainability profile, making them safer for both indoor and outdoor applications. Utilizing untreated softwoods in construction can effectively minimize harmful emissions and promote healthier indoor air quality.
Finally, the promotion of recycled and reclaimed softwoods is also on the rise. By repurposing old structures and furniture, wood can be given new life, exacerbating its sustainability value. This practice helps reduce waste, minimize resource extraction, and preserve the beauty of historical wood pieces, contributing to a circular economy in the building and design sectors.
Exotic Woods: The Luxurious Choice
Understanding the Unique Characteristics of Exotic Woods
Exotic woods are often prized for their beauty and rarity, each type offering a unique blend of color, grain patterns, and texture. These woods, sourced from various regions around the globe, bring a touch of nature's artistry into our homes and spaces. For instance, woods like Mahogany and Teak are celebrated not only for their stunning visual appeal but also for their resilience and durability, making them ideal for high-quality furniture pieces.
The characteristics of exotic woods often include distinctive features such as a pronounced grain, rich color variations, and natural oils that provide water resistance. These traits can significantly enhance the aesthetic of both indoor and outdoor projects. More importantly, the varied densities and hardness levels can affect how they are treated and finished, giving artisans and builders an expansive palette for creative expression.
Not only are exotic woods appealing, but they also come with environmental considerations. Sustainable harvesting practices are paramount to ensure that the lush forests from which these woods are sourced are preserved for future generations. Certifications from organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) offer consumers assurance that their chosen wood products have minimal environmental impact, promoting responsible use without compromising natural beauty.
When selecting exotic woods, it's essential to consider their workability. Some types might be challenging to cut, sand, and finish due to their density and resin content, while others may require specific tools for optimal results. Understanding these nuances allows craftsmen to make informed choices that enhance their projects while also respecting the wood’s unique properties.
Finally, the story behind each exotic wood type adds depth to its allure. Whether it’s the ancient growth of a Brazilian Rosewood or the unique yet fleeting availability of African Blackwood, these stories transform simple timber into cherished heirlooms. This connection to history and culture elevates the experience of choosing exotic woods to more than a mere purchase; it becomes a journey into the heart of craftsmanship.
Applications and Benefits of Using Exotic Woods
The application of exotic woods spans a vast spectrum, from luxurious furniture to intricate musical instruments. For instance, many luthiers—craftspeople specializing in stringed instruments—utilize woods like Rosewood and Mahogany to create guitars that offer exceptional sound quality and visual appeal. The unmistakable tones produced by these woods are coveted for their depth and richness, making them a prime choice for musicians and collectors alike.
Another significant advantage of using exotic woods lies in their longevity and resistance to wear and tear. Teak, renowned for its high oil content, is particularly valued for outdoor furniture construction as it withstands moisture and pests remarkably well. This durability translates into less frequent replacements, making exotic woods a long-term investment that pays off in the long run.
Moreover, it is becoming increasingly popular to incorporate exotic woods into interior design. From stunning accent walls to bespoke cabinetry, their unique attributes can transform an ordinary space into a luxurious environment. Designers often explore various finishes to enhance the rich colors and textures, allowing exotic woods to take center stage in residential and commercial settings.
Beyond aesthetics and functionality, using exotic woods also reflects a discerning taste and personal style. Homeowners and designers often seek these unique materials to stand apart from the uniformity of mass-produced products. Each slab of exotic wood tells a story of its origin, offering a distinctive mark of individuality within a market flooded with conventional options.
Finally, as a growing number of consumers become aware of their environmental impact, the demand for ethically sourced exotic woods increases. Choosing products that are responsibly harvested not only supports sustainable forestry practices but also enables consumers to enjoy these luxurious materials with a clear conscience. This approach to selecting exotic woods fosters a deep appreciation for the natural world while aligning ethics with aesthetic choices.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Project
Understanding Wood Hardness and Durability
When choosing wood for your project, one of the primary factors to consider is its hardness. Hardwoods, such as oak and maple, provide greater resistance to wear and tear, making them ideal for high-traffic areas.
In contrast, softwoods like pine and cedar, while easier to work with and often less expensive, are more vulnerable to dents and scratches. It's crucial to assess how much usage the finished piece will endure to determine the best wood type.
Furthermore, the durability of wood is influenced by its natural resistance to decay and pests. Certain woods, such as redwood and cypress, contain natural oils that help them withstand moisture, making them excellent choices for outdoor projects.
Understanding the Janka hardness rating can help you gauge the durability of various wood types. This scale measures the force required to embed a steel ball into the wood, offering a comparative guide for selection.
In summary, when considering wood hardness and durability, think not only about appearance but also how the wood will function over time. This decision affects both longevity and the overall success of your project.
Exploring Aesthetic Qualities of Different Woods
Aesthetic appeal is a significant factor in choosing wood for projects. Different woods come with unique grains, colors, and textures that can greatly affect the final look of a piece. For instance, walnut has a rich, dark hue that adds elegance and sophistication.
Conversely, lighter woods such as birch and maple provide a more contemporary and brighter appearance, fitting well in modern designs. The choice of wood can evoke certain feelings and set the tone for the overall ambiance of a space.
Additionally, the grain pattern can vary widely among wood species—from the straight grain of pine to the beautiful swirling patterns of mahogany. These natural markings contribute to the uniqueness of each piece, offering character and charm.
Staining or finishing can also enhance the visual aspect of wood, allowing for a range of looks from rustic to polished. Experimenting with different finishes can reveal the innate beauty of the wood while also protecting it.
Ultimately, aesthetic qualities are subjective, and personal preference plays a vital role in the selection process. Take time to compare samples and envision how each wood option fits into your design scheme.
Environmental Considerations in Wood Selection
In recent years, environmental impact has become a crucial consideration in the choice of wood for various projects. Sustainable wood sourcing is vital in preserving forests and protecting ecosystems. Opting for certified wood products can ensure your materials are sourced responsibly.
This includes supporting companies that engage in reforestation efforts, as well as those that harvest wood in a manner that minimizes harm to surrounding wildlife and habitats. Look for certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) which guarantees responsible forest management practices.
Furthermore, the carbon footprint of transporting different types of wood can vary significantly. Opting for locally sourced woods not only reduces environmental impact but also supports local economies, making it an eco-friendly choice for conscientious consumers.
Another aspect to consider is the chemical treatments used in processed wood products. Some treatments can release harmful VOCs (volatile organic compounds) into the environment. Choosing untreated or naturally durable woods can mitigate these concerns effectively.
By making informed choices that consider the environmental implications, you can contribute to a more sustainable future while still achieving the aesthetic and functional qualities you desire in your project.
Cost Considerations When Working with Wood
The cost of wood can vary significantly based on the type, source, and any special treatments or finishes applied. Hardwoods are generally more expensive than softwoods due to their slower growth rates and the additional labor involved in harvesting and processing them.
When budgeting for a project, it's essential to factor in not just the initial cost of the wood, but also long-term investment considerations. High-quality hardwoods may be initially pricier but can outlast cheaper alternatives, potentially leading to savings down the line.
Additionally, keep in mind the availability of certain wood types. Rare or exotic woods often come with a higher price tag due to their limited supply and increased demand. If your budget is tight, consider alternatives that offer similar aesthetic appeal but are more readily available.
In some cases, reclaimed wood can be a cost-effective option, providing not only a unique look but also helping to reduce waste. However, ensure to account for any potential costs related to refurbishing or refinishing used materials.
Ultimately, understanding the cost implications of your wood choices can aid in making better financial decisions that align with your project’s goals while allowing room for creativity and quality.
Choosing the Right Wood for Functional Needs
While beauty and quality matter, the functional requirements of your project should dictate your wood selection. Each type of wood comes with distinct properties suitable for specific applications, and understanding these can lead to better outcomes.
For furniture making, consider the weight-bearing capacity of the wood. For instance, hardwoods like oak are ideal for heavy-use items such as tables and chairs, while lighter woods like pine may be better suited for decorative pieces.
For outdoor projects, opt for woods that demonstrate resistance to moisture and weather conditions. Species like teak or cedar are often chosen for decking and outdoor furniture because of their durability against the elements.
In terms of woodworking methods, some woods are better suited for carving and detailed work while others may be more challenging to manipulate. Softwoods are often favored for intricate designs because they are easier to cut and shape.
Ultimately, understanding the functional needs of your project will guide your choice of wood, ensuring that it not only looks good but also performs well throughout its intended lifecycle.
- Innovative Multi functional Designs: Maximizing Space and Utility
- Top tips for buying second hand wooden furniture
- Eco Friendly Wood Types: Sustainable Choices for Your Home
- Sustainable Materials Not Just a Trend: The Future of Eco Friendly Solutions
- Effective Strategies for Maximizing Cost Savings in Business
- How to create a cozy bedroom with wooden furniture
- What Defines Modern Home Decor Styles in Today's Interiors?
- Pinewood Furniture Affordability: A Cost Effective Home Solution
- The Unmatched Versatility of Walnut Wood in Modern Applications
- Why walnut is a popular choice for luxury wooden furniture
- Embracing Simplicity: The Essentials of Minimalist Design for Modern Living
- Best wooden storage cabinets for organizing your home