L'extensibilité de la robotique dans les opérations de la chaîne logistique pour la croissance
La robotique dans l'exécution des commandes et la logistique

Au-delà des murs de l'entrepôt : expansion des applications robotiques
Stratégies d'extensibilité pour une chaîne logistique plus efficace L'échelonnement horizontal, également appelé extension, consiste à ajouter plus de ressources La robotique automatise rapidement une part importante des tâches routinières dans divers secteurs, de la fabrication et de la logistique à la clientèle
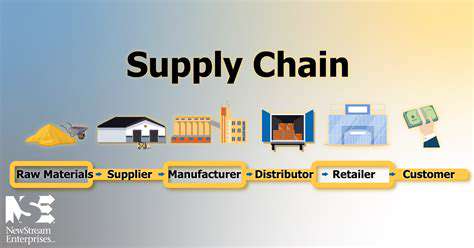
Échelonnement horizontal
L'impact de la robotique sur le travail et la dynamique de la main-d'œuvre
L'automatisation des tâches routinières
THE END
More about L'extensibilité de la robotique dans les opérations de la chaîne logistique pour la croissance
- Options de meubles en bois écologiques pour une maison durable
- Comment faire durer vos meubles en bois pendant des générations
- Meubles en bois pour bureaux à domicile, les mieux notés
- Comment associer des meubles en bois à des couleurs neutres pour une ambiance calme
- Pourquoi les meubles en bois peuvent augmenter la valeur de votre maison
- Comment équilibrer les grands meubles en bois dans les espaces ouverts
- Le guide ultime pour acheter des meubles de chambre en bois massif
- Comment combiner des meubles en bois avec une décoration vintage ?
- Comment intégrer des meubles en bois dans votre design contemporain
- Meubles en bois les plus performants pour améliorer votre espace de vie
- Robotique pour l'exécution du commerce électronique : Répondre à la demande
- Au-delà des limites humaines : L'avenir de la manutention robotisée des matériaux